|
1.
Persistent bud-scales vestigial, minute, 1.
Persistent bud-scales conspicuous,
2.
Leaves linear, acuminate, strongly revolute in upper third; 2.
Leaves oblong to linear, obtuse to acute, |
||
|
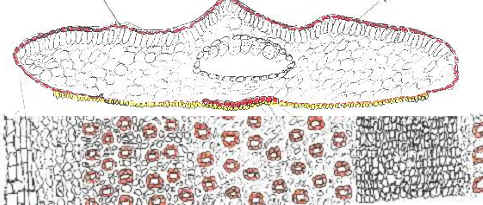
Fig. 4648 (from left to right): Taxus chinensis. Fig. 46: from Sichuan, Wang 22602 (A), with linear acute leaves. Fig. 47: from Hubei, China,,Cho 76099 (A), with oblong obtuse leaves characteristic of the species. Fig. 48: from W Hubei, Wilson 624 (A), morph with complanate leaves, showing bud-scale scars at base of branchlets, compare leaf shape with T. canadensis var. adpressa. |
||
 |
||
|
3.Dried
leaf surfaces ±concolorous, or yellowish green on abaxial surface; 3.Dried
leaf surfaces discolorous, or yellowish orange on abaxial surface; 4.
Leaves acute, apiculate, 1.5-2.0 mm broad, convex and smooth above; 4.
Leaves
obtuse,
blunt, 3.0-3.5 mm broad, plane and rugose on
|
||
 |
Fig
52 (left): Taxus scutata, from Yunnan, Tsai 18464 (A),
showing loose spreading scales at base of branchlets.
Fig.
53 (right): Taxus ocreata from Yunnan, Feng 11937 (A),
holotype, showing adnate scales at base of branchlets, cone scales, and
unattached seed.. |
 |
|
5.
Branchlets and leaves mostly not overlapping; leaves parallel at 5.
Branchlets
and leaves crisscrossing, leaves often at oblique angles,
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
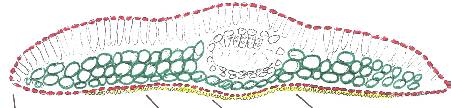
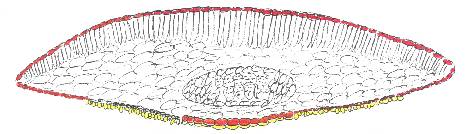
| Figs.5458:
Taxus phytonii (Figs. 5455) and T. obscura (Figs.
5658).
Fig. 54 (upper left): from Taiwan, Wilson 11154 (A, holotype). Fig.
55 (upper right):
from Yunnan, Tsai 59874 (A). Fig. 56 (lower left): from Philippines, de
Laubenfels P669 (GH). Fig. 57-58 (lower right): from Philippines, illus. of
T-sect. (Fig. 57) and view of abaxial surface of leaf (Fig. 58) showing
leaf margin (left) to midrib (right) , drawn from Curran s.n. (US).
Note contrast in color between upper and lower surfaces, and the
similarity to T. chinensis in leaf sections.
|
||